Respiratory Syncytial Virus, commonly known as RSV, is a highly contagious respiratory illness that affects the lungs and breathing passages of individuals across all age groups. While RSV typically presents as a common cold, causing mild, cold-like symptoms from which most people recover within one or two weeks, it has the potential to become serious. When a health crisis arises, telehealth becomes a vital element in delivering safe and effective healthcare. The adoption of virtual care, especially the use of telehealth for RSV management, is rapidly changing how patients monitor symptoms, receive timely advice, and prevent unnecessary exposure during contagious seasons.
Understanding Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
RSV is easily spread from person to person, often through coughing or sneezing. In most regions of the U.S., RSV outbreaks are seasonal, typically beginning in the fall and reaching their peak during the winter months.
Who is at High Risk?
Although RSV infection is widespread—most young children have been infected by the time they are two years old—the virus poses the greatest danger to specific populations. These high-risk groups are more likely to develop severe disease and require hospitalization:
- Infants and Young Children: RSV is the leading cause of infant hospitalization in the U.S.. Infants, especially during their first infection, may develop lower respiratory tract disease (LRTD) such as pneumonia or bronchiolitis (swelling of the small airways). Premature infants and those with chronic lung disease of prematurity face the highest risk of complications.
- Older Adults (Ages 60+): In adults, RSV can lead to LRTD, hospitalization, and even death.
- Adults with Chronic Conditions: Individuals with a weakened immune system, chronic heart or lung disease, or diabetes are at increased risk of severe RSV infection.
At-Home Treatment and Warning Signs
Most mild RSV infections resolve on their own within two weeks, requiring only supportive care at home. Treatment for both children and adults focuses on supportive measures:
- Hydration: Getting enough fluid (water and other fluids) to stay hydrated is essential.
- Symptom Management: Treating pain and fever as suggested by a healthcare provider.
It is crucial to talk to a healthcare provider if cold-like symptoms worsen progressively, particularly if they begin to affect breathing, hydration, or the ability to eat. For respiratory illnesses like RSV, COVID-19, or the flu, tests are available that a provider can order, or in some cases, home collection tests can be utilized.
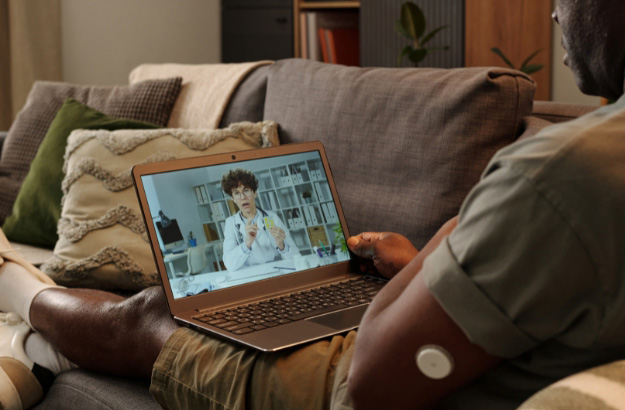
The Essential Role of Telehealth for RSV Management
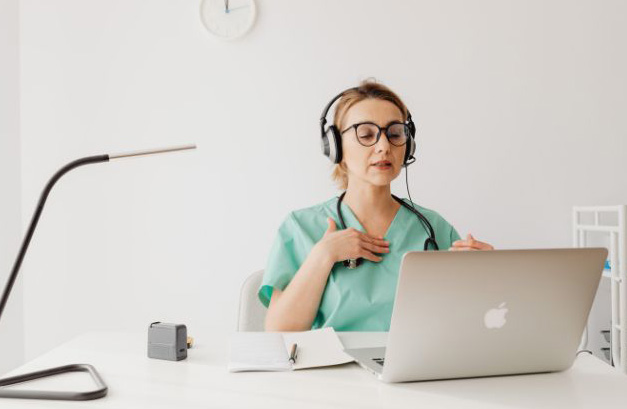

During seasonal outbreaks, virtual care is vital, as patients are strongly encouraged to avoid coming to the office or hospital unless their condition is clinically necessary. This is where the effective use of telehealth for RSV becomes indispensable, allowing clinicians to screen patients, manage symptoms, and triage higher-risk cases remotely. Respiratory therapists (RTs), for example, are able to provide telehealth services and utilize Medicare benefits to facilitate this care.
Telehealth enhances patient experience and improves access to care. By transitioning certain visits from in-person to virtual encounters, healthcare providers can focus on those requiring face-to-face attention while still managing a high volume of respiratory concerns. Telehealth also serves as a key strategy for reducing face-to-face cancellations and same-day no-shows.
Telehealth Modalities for RSV Support
Telehealth for RSV utilizes distinct technologies, moving beyond simple phone calls to offer effective clinical interactions:
- Synchronous Virtual Visits: This refers to the delivery of health information in real-time. This allows for a live discussion between the patient (or parent/caregiver) and the provider, essential for initial assessment or when symptoms are worsening. A synchronous virtual visit is a real-time clinical encounter using technology that supports live communication.
- Asynchronous Screening and Check-ins: Asynchronous tools, often chat-based, allow a patient to share health information that a provider reviews later. These tools can be customized to gather vital information about a patient’s symptoms or health status, acting as an important clinical screening tool that can alleviate pressure on administrative staff. Furthermore, a Virtual Check-in allows for a short, patient-initiated touch-base with a clinician following a prior in-person or virtual visit.
- Remote Monitoring: This involves the real-time evaluation of a patient’s clinical status. Newer technologies, such as mobile applications on devices, allow for a wider breadth of possibilities in tracking patient data remotely. For managing a respiratory condition like RSV, remote monitoring is crucial for tracking metrics related to a patient’s health status, especially for vulnerable individuals.
Prevention and Protecting Vulnerable Populations
Beyond supportive care and remote monitoring via telehealth for RSV, prevention is paramount, especially for high-risk groups. The FDA has approved several methods to protect against the severity of the virus.
Immunization Options
Healthcare providers have guidance available concerning RSV immunization for infants, young children (19 months and younger), pregnant women, and adults. Options include:
- Infants and Young Children: Protection is available through monoclonal antibodies (such as nirsevimab and palivizumab), which are laboratory-made proteins that mimic the immune system’s ability to fight off viruses.
- Pregnant Individuals: A vaccine (ABRYSVO) is approved for pregnant individuals between 32 and 36 weeks gestational age to protect infants from RSV LRTD and severe LRTD from birth through 6 months of age.
- Adults: Three FDA-approved vaccines (ABRYSVO, Arexvy, and mRESVIA) are available to prevent RSV LRTD in adults ages 60 and older. ABRYSVO and Arexvy are also approved for certain individuals aged 18 through 59 who are at increased risk for LRTD caused by RSV.
A Step Forward in Respiratory Care
Telehealth for RSV provides safe and effective pathways to manage this common, yet potentially serious, respiratory virus. By utilizing synchronous visits for acute evaluation, asynchronous tools for screening and initial triage, and remote monitoring for ongoing clinical surveillance, providers can ensure high-risk patients receive necessary care while limiting exposure risks. As health experts predict that virtual consumption of healthcare services will continue to grow significantly, integrating telehealth into respiratory care protocols ensures timely access and efficient health outcomes.We encourage you to talk to a healthcare provider to determine the best preventative measures for you and your family, and to learn how virtual visits can be incorporated into your care plan. Contact us today to book an appointment and discover the convenience and effectiveness of utilizing telehealth for RSV management and other respiratory health needs.
Explore related articles to see the impact of telehealth on your care:



